|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Main Relay Technical details
What is the main relay?
The main relay (which consists of two relays that are remotely operated as a switch) is a device that opens or closes battery current of up to 40 Amps each. The main relay is in direct control from another device usually the ignition switch or ECU. During operation the main relay closes the fuel injectors and the ECU, then closes the fuel pump in this sequence. The role of the main relay serves other purposes as well. Other devices can shutdown the main relay such as when the fuel runs out, or in some vehicle when the car is in a collision. If the battery cables are reversed the main relay also shuts down.
How do I identify the main relay?
Look for the "RELAY ASS'Y. MAIN." (ASS'Y. is short for assembly.)
Physically moving Fuel: - Fuel system
-
The fuel begins its journey from the fuel tank and into the fuel pump then to the fuel filter and into to the gates of the fuel injectors. The fuel flow can be intterupted by several factors. During such times when the car is in a collusion, stalling, running out of gas or (on some vehicles) overturned the main relay shuts off the fuel pump when the ECU (main computer) or the inertia switch (on the 96+ Civic) tells it to. The inertia switch can be reset by pressing the button. The distributor and the ignition switch also shuts off the fuel supply.
-
Sometimes a defective main relay will start the car for a second then quickly dies out. At this moment, the rpm could register 1600 before the engine completely dies. The car will then crank but won't start. This is due to the remaining fuel pressure in the fuel line. Many people complained that the problem is creating anxieties because they are afraid of being stranded or ending up with an expensive repair bill. To reduce your anxieties just flip thru the pages.
-
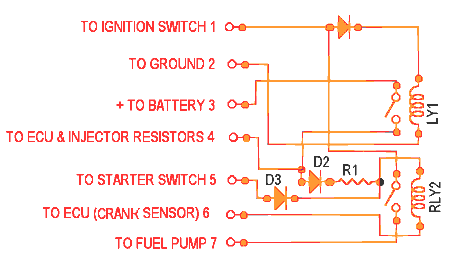
Above is a diagram of the main relay internal circuits.
Electronically controlling fuel: ECU.
-
The ECU controls the main relay by grounding the fuel pump relay for 2 seconds when the ignition is switch ON. Upon START the ECU grounds the fuel pump relay until START releases. While the car is in operation the ECU constantly sends ground to the the fuel pump relay. The ECU is constantly on standby, ready to deactivate the fuel pump.
-
The ECU monitors the fuel injector power supply source from the main relay. If none are found the check engine light will come on and stay on.
Electronically controlling fuel: Main relay.
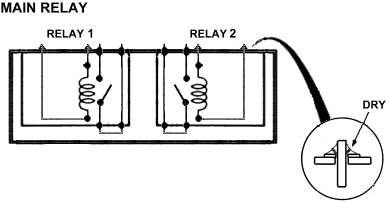
-
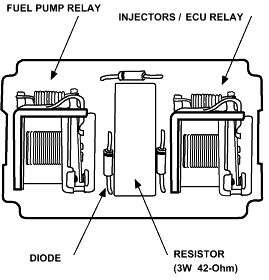
Technically, the main relay is made up of two relays, one for the injectors/ECU and one for the fuel pump. To prove this you can hear two clicks almost in sync when you turn on the key. The relay sits on a PC board inside a plastic case, The PCB board contains a resistor and some diodes.
-
Usually the injector/ECU relay may be the second to fail, most always from a dry joint. If the injector/ECU relay fails, a "check engine light" will turn on longer than usual after the ignition is first turned to ON and no clicks are heard from the main relay. And diagnostic trouble code (DTC) 16 may be sought, which should point to a fuel injector open circuit problem - which is most likely a main relay problem. At the same time the fuel pump won't run.
-
The relay will close, pressurizing the fuel rail for 2 seconds when the ignition is switch ON. After this time the fuel relay will open - this can be heard as a second "click." The second click means that the relay is working but doesn't necessarily mean that the relay has powered the fuel pump.
-
Switching ignition to START will close the relay, pressurizing the fuel rail until the ignition key is released from START. The ECU will (in addition to obtaining battery power from the battery post) will also get it's battery power from the main relay. If no battery power is found a "check engine light" will come on and stay on (as stated before) and the car won't start and won't produce any sparks on cars with an electronic timing control. See ecu.html for details on why your engine light is misbehaving.
-
The main relay supplies the battery voltage to the injector resistors (and on some cars, the heated oxygen sensor) whenever the ignition is switched on .
-
Do not run the starter for longer than 20 seconds at a time. Doing this may burn out the starter motor or starter motor brushes and the commutator. Crank for less than 20 seconds if you are attempting to obtain a DTC code. Continuously running the starter isn't the right thing to do, since you can run the battery down and reduce your battery and starter life. Instead give a slight banging with a fist on the left dash board, cool the car down or give the main relay CPR (Conk it, Poke it, Rattle it.)
The main relay assembly: How to remove.
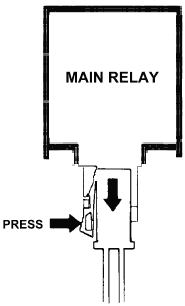
-
The main relay is held together to the casing (housing) using clips that can be pried open with your fingers or a screw driver. The 86-89 accord main relay location is very deep so it's a good idea to leave the casing where it is while just removing the the "guts" of the main relay for a replacement or repairs. The 90-93 Accord location is easier to remove so it's better to remove the relay as a unit. This also prevent accidental shorts.
-
The main relay can be difficult to remove when it's located very deep inside the dashboard and very high up. Most often, it isn't necessary to remove the dashboard to get to the main relay. All you need to remove are the dashboard lower covers. To locate the main relay, turn on the ignition and listen for the clicks. The relay that clicks twice (within 2 seconds apart) when the ignition is turn to "ON" is the relay you want.
-
Removing the harness connector is easier done with a watch repair flat-head screw driver.
Main Relay |
|
| Relay manufacture | Mitsuba, made in Japan. |
| Numbers of relays inside | Two |
| Part | Part Number |
Mitsuba RZ-0063 or .. 0028 ..0064 for
|
39400-SH3-003 |
Mitsuba RZ-0105 for ACURA
|
|
| One Resistor | 3W, 42-Ohm. Reasons: reduce relay heat buildup, reduce current, reduce transistor stress. |
| Three Diodes | Probable reason: Prevents ECU damage during accidental reversing of the battery cables. |
| Terminals | 7 terminals , Legend and TL has more terminals |
| Operating Relay Temperature | -30 to 85 degrees Celsius. |
| Rated relay Amps | 40A |
| Voltages | 12V |
| Max. Switching Voltage | |
| Installed on Carburetor models | No |
| Expected life span | 8-10 years or slightly above 100k miles |
| Price ranges | $28-$75USD, |